
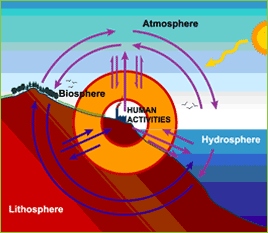
Those systems require a significant place on the ground, but, in addition to an easy and a cheap exploitation cost, they also make possible aggressive CO 2 and hydrogen sulfide (H 2S) removal. This elimination can be carried out by cascade or spraying open-air systems (for an acceptable maximum content of Fe 2+ of 7mg.L -1) known as gravitating systems. The stage of precipitation by chemical oxidation can also be carried out with the stronger oxidants such as the chlorine dioxide (ClO 2), ozone (O 3) or the potassium permanganate (KMnO 4). The precipitate is then separated from water by filtration on sand or decantation. Thus, the ferrous iron is oxidized in ferric iron, which precipitates in iron hydroxide, Fe(OH) 3. In the case of acid water, the treatment could be supplemented by a correction of the pH. The elimination of the ferrous iron, by physical-chemical way, is obtained by raising the water redox potential by oxidation thanks to oxygen of the air and this by simple ventilation. However ground waters are naturally anaerobic: so iron remains in solution and therefore it is important to remove it for a water use. Usually groundwater has a low oxygen content, thus a low redox potential and low pH (5.5- 6.5) The form of iron in water depends on the water pH and redox potential, as shown in the Pourbaix diagram of Iron below. In aerated water, the redox potential of the water is such as it allows an oxidation of the ferrous iron in ferric iron which precipitates then in iron hydroxide, Fe(OH) 3, thus allowing a natural removal of dissolved iron. It can also be at the origin of corrosion in drains sewers, due to the development of microorganisms, the ferrobacteries. Iron also gives a metallic taste to water, making it unpleasant for consumption. Indeed, iron gives a rust color to the water, which can stain linen, sanitary facilities or even food industry products. In general, iron does not present a danger to human health or the environment, but it brings unpleasantness of an aesthetic and organoleptic nature. The occurrence of iron in water can also have an industrial origin mining, iron and steel industry, metals corrosion, etc. It occurs naturally in water in soluble form as the ferrous iron (bivalent iron in dissolved form Fe 2+ or Fe(OH) +) or complexed form like the ferric iron (trivalent iron: Fe 3+ or precipitated as Fe(OH) 3). Iron Removal by physical-chemical ways Iron is one of the most abundant metals of the Earth's crust.
Separation and Concentration Purification Request.Plant Inspection & Process Optimalisation.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
